|
||||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||

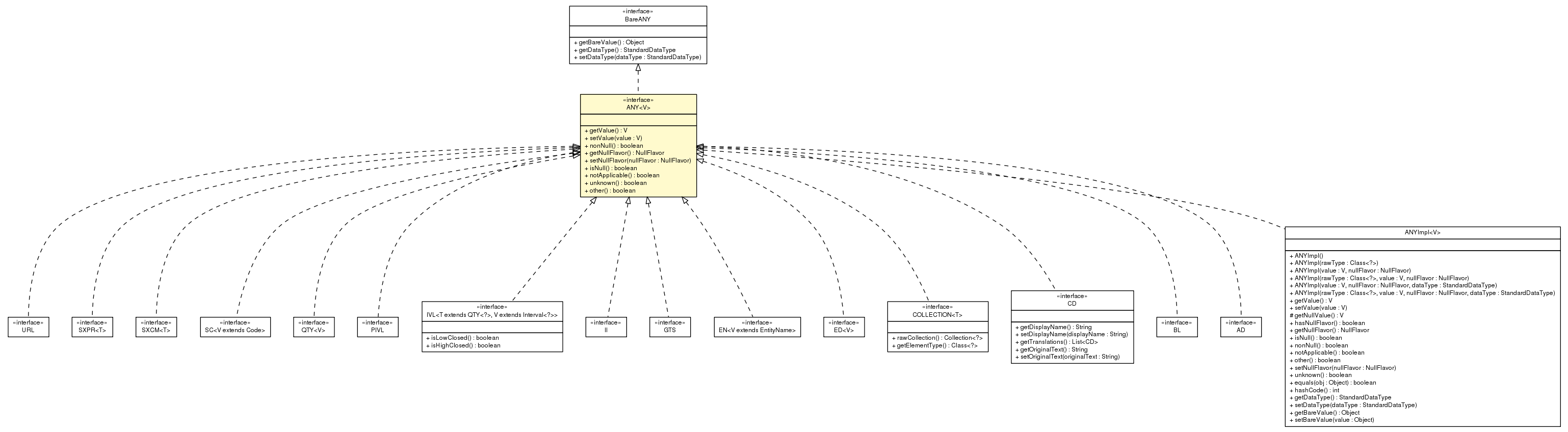
V - the underlying java datatypepublic interface ANY<V>
ANY Hl7 datatype.
Defines the basic properties of every data value.
This is an abstract type, meaning that no value can be just a data value without belonging to any concrete type. Every concrete type is a specialization of this general abstract DataValue type.
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
NullFlavor |
getNullFlavor()
If a value is an exceptional value (NULL-value), this specifies in what way and why proper information is missing. |
V |
getValue()
Returns the value. |
boolean |
isNull()
Indicates that a value is an exceptional value, or a NULL-value. |
boolean |
nonNull()
Indicates that a value is a non-exceptional value of the data type. |
boolean |
notApplicable()
A predicate indicating that this exceptional value is of nullFlavor not-applicable (NA), i.e., that a proper value is not meaningful in the given context. |
boolean |
other()
A predicate indicating that this exceptional value is of nullFlavor other (OTH), i.e., that the required value domain does not contain the appropriate value. |
void |
setNullFlavor(NullFlavor nullFlavor)
Sets a null flavor on the object. |
void |
setValue(V value)
Sets a value on the ANY object. |
boolean |
unknown()
A predicate indicating that this exceptional value is of nullFlavor unknown (UNK). |
| Methods inherited from interface ca.infoway.messagebuilder.datatype.BareANY |
|---|
getBareValue, getDataType, setDataType |
| Methods inherited from interface ca.infoway.messagebuilder.datatype.nullflavor.NullFlavorSupport |
|---|
hasNullFlavor |
| Method Detail |
|---|
V getValue()
Returns the value.
void setValue(V value)
Sets a value on the ANY object.
value - the value to set on this ANY objectboolean nonNull()
Indicates that a value is a non-exceptional value of the data type.
When a property, RIM attribute, or message field is called mandatory this means that any non-NULL value of the type to which the property belongs has a non-NULL value for that property, in other words, a field may not be NULL, providing that its container (object, segment, etc.) is to have a non-NULL value.
NullFlavor getNullFlavor()
If a value is an exceptional value (NULL-value), this specifies in what way and why proper information is missing.
The null flavors are a general domain extension of all normal data types. Note the distinction between value domain of any data type and the vocabulary domain of coded data types. A vocabulary domain is a value domain for coded values, but not all value domains are vocabulary domains.
The null flavor "other" is used whenever the actual value is not in the required value domain, this may be, for example, when the value exceeds some constraints that are defined too restrictive (e.g., age less than 100 years.)
NOTE: NULL-flavors are applicable to any property of a data value or a higher-level object attribute. Where the difference of null flavors is not significant, ITS are not required to represent them. If nothing else is noted in this specification, ITS need not represent general NULL-flavors for data-value properties.
Some of these null flavors are associated with named properties that can be used as simple predicates for all data values. This is done to simplify the formulation of invariants in the remainder of this specification.
Remember the difference between semantic properties and representational "components" of data values. An ITS must only represent those components that are needed to infer the semantic properties.
The null-flavor predicates nonNull, isNull, notApplicable, unknown, and other can all be inferred from the nullFlavor property.
getNullFlavor in interface NullFlavorSupportvoid setNullFlavor(NullFlavor nullFlavor)
Sets a null flavor on the object.
setNullFlavor in interface NullFlavorSupportnullFlavor - the null flavor to setboolean isNull()
Indicates that a value is an exceptional value, or a NULL-value. A null value means that the information does not exist, is not available or cannot be expressed in the data type's normal value set.
Every data element has either a proper value or it is considered NULL. If (and only if) it is NULL, the isNull provides more detail as to in what way or why no proper value is supplied.
boolean notApplicable()
A predicate indicating that this exceptional value is of nullFlavor not-applicable (NA), i.e., that a proper value is not meaningful in the given context.
boolean unknown()
A predicate indicating that this exceptional value is of nullFlavor unknown (UNK).
boolean other()
A predicate indicating that this exceptional value is of nullFlavor other (OTH), i.e., that the required value domain does not contain the appropriate value.
|
||||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||